Core Data
Core Data 是一個設計用來儲存資料的框架,背後操作的雖然仍是 SQLite ,但其簡化了資料庫的處理,讓你不用了解 SQL 指令也可以快速的為應用程式建立並使用資料庫。
如果你是第一次接觸資料庫相關的知識,以下會簡單的介紹一下運作方式:
資料庫顧名思義,是一個用來儲存大量資料的容器,以現實生活來說,最簡單的資料庫可以用一個文件夾來比喻。
例如,一個文件夾是用來存放所有學生的資訊,裡頭每一頁都代表一名學生的資訊,每一名學生都會有各式各樣的資訊,像是姓名、座號、血型或出生年月日等等。
以上例子了解後,我們將它與 Core Data 的內容對比在一起,如下:
| 現實生活 | 文件夾 | 每一頁學生 | 學生的各個資訊 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Data | Entity (實體) | 每筆資料 | Attribute (屬性) |
所以假設當我們要為 Core Data 新增一筆資料時,這個步驟為:
- 首先找出要操作的 Entity (拿出文件夾)。
- 接著將要新增的一筆資料的各個 attribute 設定好(拿出一張新的紙,將一位新學生的基本資料填上)。
- 在 Entity 增加這筆資料(為文件夾加入新的一頁,也就是新增這位學生的資訊)。
- 儲存這個增加資料的動作(文件整理完畢,將文件夾關上)。
Hint
- 如果以關聯式資料庫的概念來對比的話, Core Data 的 Entity 與 Attribute 大約可以比對到 Table (資料表)與 Field (欄位)。
- 本節僅會介紹基本的功能,實際的資料庫操作可能會更為複雜。
以下會先介紹在應用程式中如何加入 Core Data ,接著會介紹如何新增、讀取、更新與刪除資料,最後會將 Core Data 功能獨立寫在一個類別中,來把實際操作 Core Data 的程式碼封裝起來。
加入 Core Data
首先在 Xcode 裡,新建一個 Single View Application 類型的專案,取名為 ExCoreData 。建立專案的過程中,請記得將Use Core Data打勾,如下圖:

設定 Entity 與 Attribute
建立好專案後,可以看到左邊的專案檔案列表中,有一個名為ExCoreData.xcdatamodeld的檔案,這是用來設定 Entity 與 Attribute 的檔案。請點開這隻檔案並點擊下方的Add Entity按鈕,如下圖:
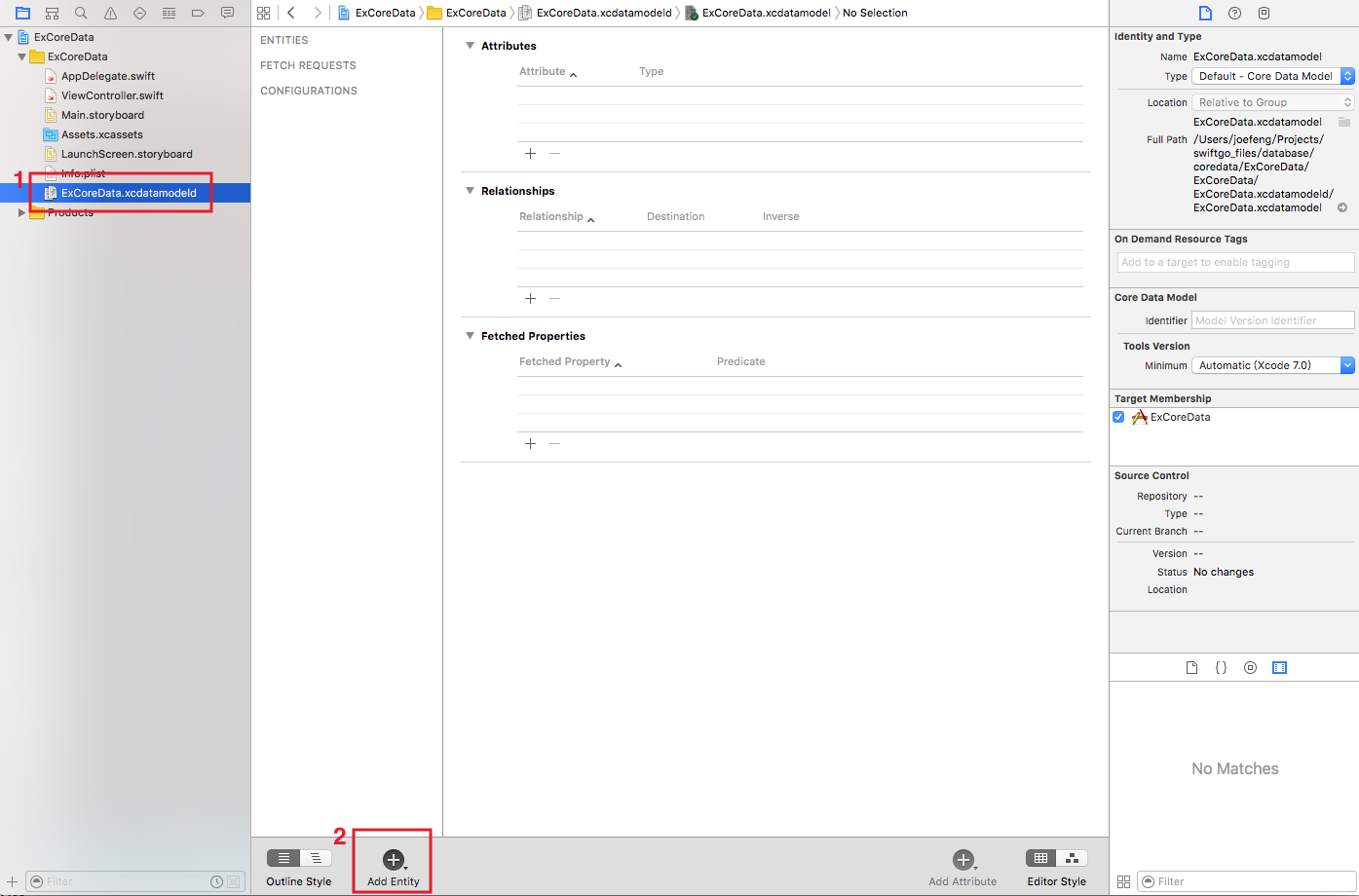
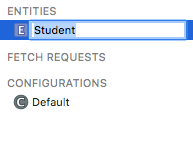
接著將這個 Entity 命名為 Student (點擊兩下可命名),如下圖:
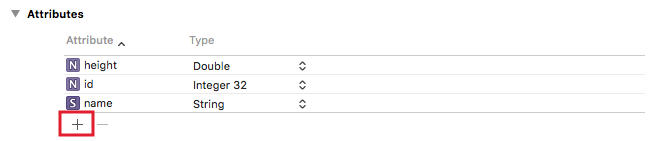
增加完 Entity 後,接著點擊 Attributes 的加號按鈕,依序增加三個 Attribute ,分別為 id, name, height , Type 也就是每一個 Attribute 的類型,依序設定為 Integer 32, String, Double ,如下圖:
建立 Entity 的類別
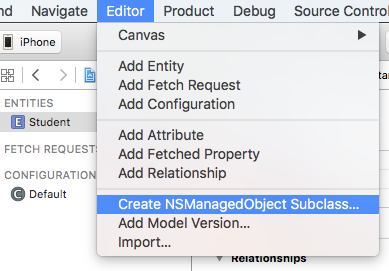
為了要讓程式碼中可以使用這個 Entity ,接著要建立一個繼承自 NSManagedObject 的 Student 類別。請點選 Xcode 工具列中的Editor > Create NSManagedObject Subclass...來讓 Xcode 為我們自動生成相關檔案,如下:
接著兩個步驟都是按Next繼續,如下面兩張圖:
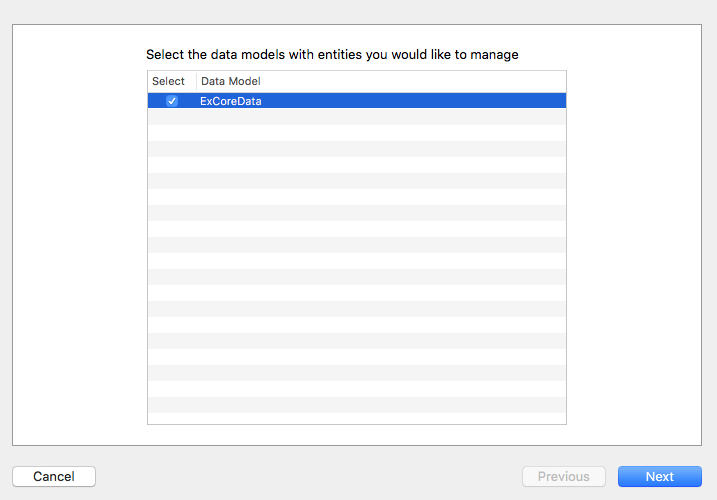
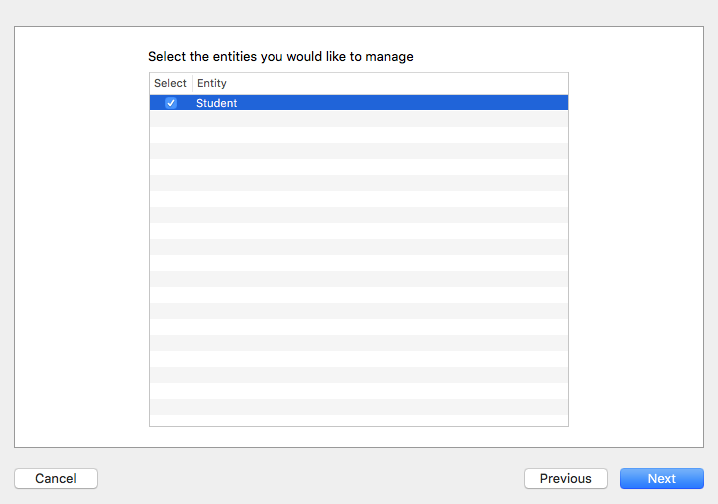
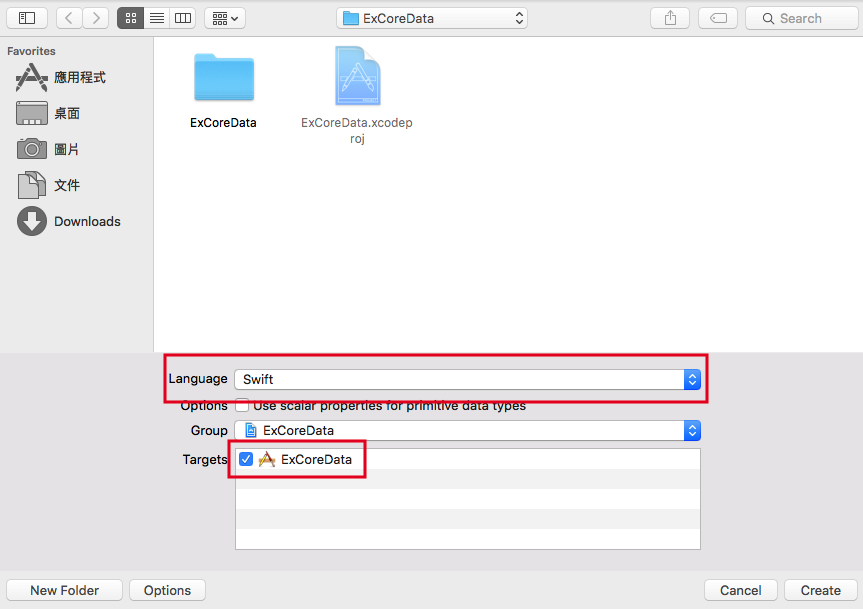
建立檔案的存放路徑時,記得 Language 要選擇 Swift ,並記得 Targets 要打勾,如下圖:
建立完畢後,就會在左側檔案列表中看到兩隻新檔案,分別為一個繼承自 NSManagedObject 的 Student 類別,以及這個類別的擴展,如下:
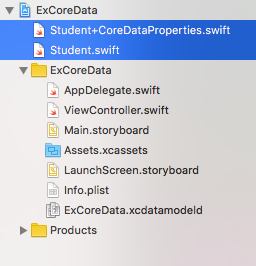
這樣就完成了加入 Core Data 的步驟。
使用 Core Data
接著進入到程式碼的部份,首先宣告一個用來操作 Core Data 的常數:
// 用來操作 Core Data 的常數
let moc = (UIApplication.sharedApplication().delegate
as! AppDelegate).managedObjectContext
在建立專案時如果有打勾Use Core Data,建立完成後會為你自動生成相關程式碼在AppDelegate.swift中,裡面你可以看到操作的資料庫仍然是一個 sqlite 檔案,以及其他建立好的設定。
所以上述程式是以委任的方式,取得AppDelegate.swift的屬性managedObjectContext,來操作 Core Data 。
接著宣告一個 Entity 的名稱(記得要與前一小節設定的名稱一樣),以供後續使用:
let myEntityName = "Student"
新增資料
新增資料的方式如下:
// insert
let student =
NSEntityDescription.insertNewObjectForEntityForName(
myEntityName, inManagedObjectContext: moc)
as! Student
student.id = 1
student.name = "小強"
student.height = 173.2
do {
try moc.save()
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
上述程式經由NSEntityDescription類別的insertNewObjectForEntityForName()方法來新增一筆資訊,這個方法的兩個參數分別為 Entity 名稱及一開始宣告的用來操作 Core Data 的常數。
接著這個方法回傳一個 Student 的實體並指派給常數student,這時的進度就與稍前文件夾例子中的 2. 拿出一張新的紙 相同,所以接著要將student的各個 attribute 設定好(將一位新學生的基本資料填上)。
目前已經有一筆新資料了,但尚未將這筆資料儲存,所以接著要使用常數moc的save()方法來儲存資料,而因為這個方法是一個拋出函式,所以使用do-catch語句來定義錯誤的捕獲。
如果沒有發生錯誤,即是順利儲存一筆新的資料。
讀取資料
讀取資料的方式如下:
// select
let request = NSFetchRequest(entityName: myEntityName)
// 依 id 由小到大排序
request.sortDescriptors =
[NSSortDescriptor(key: "id", ascending: true)]
do {
let results =
try moc.executeFetchRequest(request) as! [Student]
for result in results {
print("\(result.id). \(result.name!)")
print("身高: \(result.height)")
}
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
要取得資料首先必須使用類別NSFetchRequest來設置要取得的 Entity ,以用來建立一個取得資料的請求( request )。
接著其實可以直接取得資料,但這個例子使用了屬性sortDescriptors額外設定取得資料排序的方式,這是一個型別為[NSSortDescriptor]的陣列,可以填入多個排序方式,上述例子中只填入一個NSSortDescriptor(key: "id", ascending: true),兩個參數依序為要依照哪一個 attribute 排序以及是否由小排到大。所以這個例子為:取得的資料要依照 id 的值由小排到大。(與關聯式資料庫的 order by 類似。)
最後使用moc的方法executeFetchRequest()來取得資料,這個方法的參數就是由類別NSFetchRequest返回指派的常數。順利取回的資料會是一個型別為[Student]的陣列,便可以使用for-in迴圈來依序取得每筆資料。
更新資料
更新資料的方式如下:
// update
let request = NSFetchRequest(entityName: myEntityName)
request.predicate = nil
let updateID = 1
request.predicate =
NSPredicate(format: "id = \(updateID)")
do {
let results =
try moc.executeFetchRequest(request)
as! [Student]
if results.count > 0 {
results[0].height = 155
try moc.save()
}
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
更新資料前需要先讀取資料,所以一開始與稍前的程式碼類似,同樣使用類別NSFetchRequest來設置要取得的 Entity ,以建立一個取得資料的請求( request )。
除了稍前介紹可以額外設定排序方式,這邊示範另一個屬性predicate,這可以讓你設定取得資料的條件,例如這個例子設定條件為NSPredicate(format: "id = 1"):取得id = 1的資料。(與關聯式資料庫的 where 條件類似。)
接著與稍前例子一樣,使用moc.executeFetchRequest()來取得資料,而這個例子因為是要更新資料,所以在順利取得後,將要更新的屬性設置完畢,再以moc.save()來儲存這個更新的動作。
Hint
- 這個例子中的
request.predicate = nil不是必須的,是用來提醒你,如果有多個查詢資料庫的需求,在每次新的查詢要設定屬性predicate前,要先將其設置為nil以清空查詢條件。 - 如果查詢條件的類型為 text ,記得參數
format中要將該值以單引號'包含起來,像是NSPredicate(format: "name = '小強'")這樣。
刪除資料
刪除資料方式如下:
// delete
let request = NSFetchRequest(entityName: myEntityName)
request.predicate = nil
let deleteID = 3
request.predicate =
NSPredicate(format: "id = \(deleteID)")
do {
let results =
try moc.executeFetchRequest(request)
as! [Student]
for result in results {
moc.deleteObject(result)
}
try moc.save()
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
刪除資料與更新資料的方式類似,所以請參考稍前的例子,主要注意到moc.deleteObject()這個方法是用來刪除資料,而最後仍然要記得使用moc.save()來儲存這個刪除的動作。
以上便為基本操作 Core Data 的方式。
將 Core Data 功能獨立出來
這一小節會將 Core Data 功能獨立寫在一個類別中,來把實際操作 Core Data 的程式碼封裝起來,這樣一般在使用時就不會使用到 Core Data 相關的類別或函式。
首先以新增檔案的方式加入一個.swift檔案,命名為CoreDataConnect.swift,記得檔案類型要選擇Swift File:
iOS > Source > Swift File
接著打開這隻檔案,先建立一個類別及其內的屬性跟建構器:(記得要先import CoreData)
class CoreDataConnect {
var moc :NSManagedObjectContext!
typealias MyType = Record
init(moc:NSManagedObjectContext) {
self.moc = moc
}
}
上述程式中,使用typealias的特性設置一個型別別名,這樣在後續的資料操作,使用這個別名MyType即可,不用使用原始的 Entity 名稱Record。
新增資料
首先在上面這個類別中,定義新增資料的方法:
// insert
func insert(myEntityName:String,
attributeInfo:[String:String]) -> Bool {
let insetData =
NSEntityDescription.insertNewObjectForEntityForName(
myEntityName, inManagedObjectContext: self.moc)
as! MyType
for (key,value) in attributeInfo {
let t =
insetData.entity.attributesByName[key]?.attributeType
if t == .Integer16AttributeType
|| t == .Integer32AttributeType
|| t == .Integer64AttributeType {
insetData.setValue(Int(value),
forKey: key)
} else if t == .DoubleAttributeType
|| t == .FloatAttributeType {
insetData.setValue(Double(value),
forKey: key)
} else if t == .BooleanAttributeType {
insetData.setValue(
(value == "true" ? true : false),
forKey: key)
} else {
insetData.setValue(value, forKey: key)
}
}
do {
try moc.save()
return true
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
return false
}
這個方法與稍前介紹新增資料時的程式碼一樣,有一點要注意的是,這邊因為其中一個傳入的參數:要新增的 attribute 及其值,是統一以字串傳入,所以這個方法內需要根據 attribute 的類型student.entity.attributesByName[key]?.attributeType來轉換型別為 Int, Double, Bool 或是原本的字串,再以方法
setValue(_,forKey:)設置值並儲存。
讀取資料
接著定義讀取資料的方法:
// select
func fetch(myEntityName:String, predicate:String?,
sort:[[String:Bool]]?, limit:Int?) -> [MyType]? {
let request = NSFetchRequest(
entityName: myEntityName)
// predicate
if let myPredicate = predicate {
request.predicate =
NSPredicate(format: myPredicate)
}
// sort
if let mySort = sort {
var sortArr :[NSSortDescriptor] = []
for sortCond in mySort {
for (k, v) in sortCond {
sortArr.append(
NSSortDescriptor(
key: k, ascending: v))
}
}
request.sortDescriptors = sortArr
}
// limit
if let limitNumber = limit {
request.fetchLimit = limitNumber
}
do {
let results =
try moc.executeFetchRequest(request)
as! [MyType]
return results
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
return nil
}
讀取資料的方法將講過的兩個額外查詢功能:查詢條件predicate與排序方式sortDescriptors以及限制查詢筆數fetchLimit都加入,並將其都設為可選型別,這樣如果不需要時填入nil即可,返回的是一個型別為[Student]的陣列。
更新資料
定義更新資料的方法:
// update
func update(myEntityName:String, predicate:String?,'
attributeInfo:[String:String]) -> Bool {
if let results = self.fetch(
myEntityName,
predicate: predicate, sort: nil, limit: nil) {
for result in results {
for (key,value) in attributeInfo {
let t =
result.entity.attributesByName[key]?.attributeType
if t == .Integer16AttributeType
|| t == .Integer32AttributeType
|| t == .Integer64AttributeType {
result.setValue(
Int(value), forKey: key)
} else if t == .DoubleAttributeType
|| t == .FloatAttributeType {
result.setValue(
Double(value), forKey: key)
} else if t == .BooleanAttributeType {
result.setValue(
(value == "true" ? true : false),
forKey: key)
} else {
result.setValue(
value, forKey: key)
}
}
}
do {
try self.moc.save()
return true
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
}
return false
}
這邊會先以讀取資料方法,取得要更新的資料,再將各 attribute 設置好後才再儲存,與新增資料相同,統一以字串傳入,所以需要根據 attribute 類型來轉換型別。
刪除資料
定義刪除資料的方法:
// delete
func delete(myEntityName:String, predicate:String?)
-> Bool {
if let results = self.fetch(myEntityName,
predicate: predicate, sort: nil, limit: nil) {
for result in results {
self.moc.deleteObject(result)
}
do {
try self.moc.save()
return true
} catch {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
}
return false
}
這邊會先以讀取資料方法,取得要刪除的資料,再將取得的資料刪除,並儲存刪除的動作。
使用這個類別
將 Core Data 功能寫在一個類別後,接著將 ViewController.swift 的viewDidLoad()內容改寫為:
let myEntityName = "Student"
let coreDataConnect = CoreDataConnect(moc: self.moc)
// auto increment
let myUserDefaults =
NSUserDefaults.standardUserDefaults()
var seq = 1
if let idSeq = myUserDefaults.objectForKey("idSeq")
as? Int {
seq = idSeq + 1
}
// insert
let insertResult = coreDataConnect.insert(
myEntityName, attributeInfo: [
"id" : "\(seq)",
"name" : "'小強'",
"height" : "176.1"
])
if insertResult {
print("新增資料成功")
myUserDefaults.setObject(seq, forKey: "idSeq")
myUserDefaults.synchronize()
}
// select
let selectResult = coreDataConnect.fetch(
myEntityName,
predicate: nil, sort: [["id":true]], limit: nil)
if let results = selectResult {
for result in results {
print("\(result.id). \(result.name!)")
print("身高: \(result.height)")
}
}
// update
let updateName = "二強"
var predicate = "name = '\(updateName)'"
let updateResult = coreDataConnect.update(
myEntityName,
predicate: predicate,
attributeInfo: ["height":"162.2"])
if updateResult {
print("更新資料成功")
}
// delete
let deleteID = 2
predicate = "id = \(deleteID)"
let deleteResult = coreDataConnect.delete(
myEntityName, predicate: predicate)
if deleteResult {
print("刪除資料成功")
}
上述程式可以發現已經看不到操作 Core Data 相關的類別與函式,因為已經都寫在 CoreDataConnect.swift 中了。
其中要提醒的是,因為 Core Data 沒有提供 auto increment 的功能(每次新增資料都自動為其中一個 attribute 遞增的功能),所以這邊以NSUserDefaults儲存一個數值來手動建立 auto increment 功能,每次新增資料成功時都將這個值加一,下次新增時會再取出這個值來使用。
以上便為本節範例的內容。
範例
本節範例程式碼放在 database/coredata